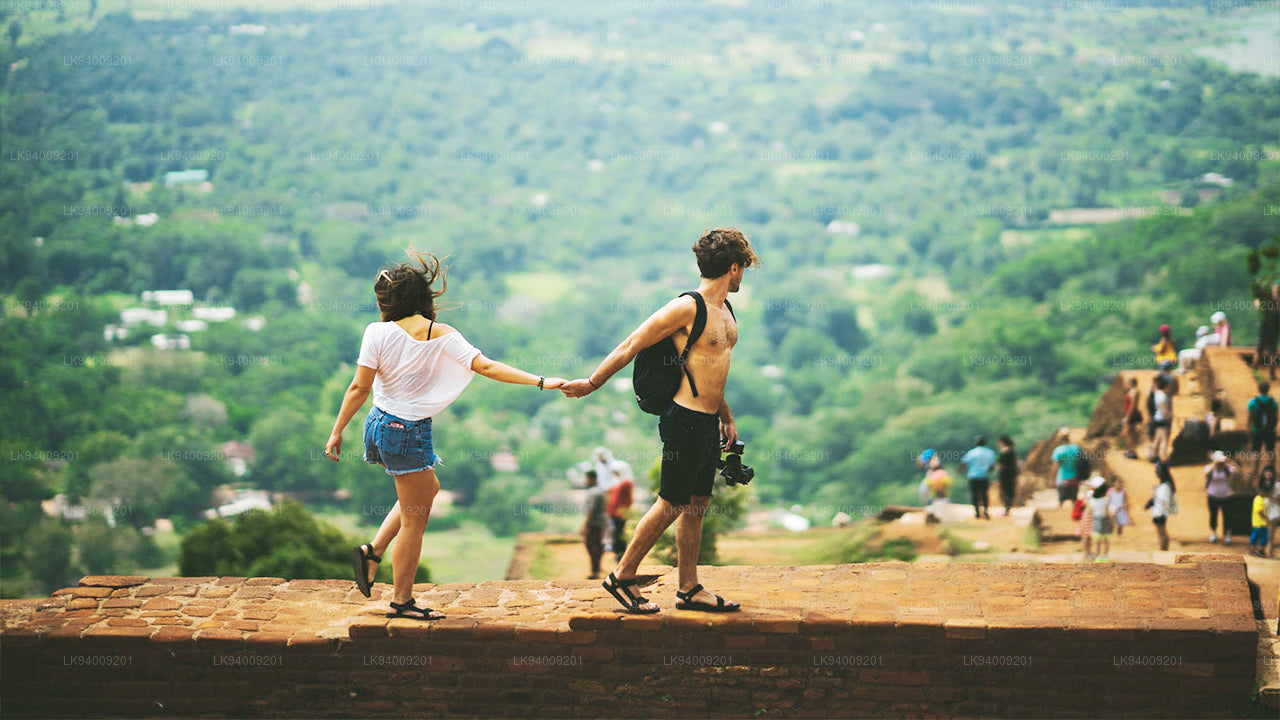
Dambulla City
Journey into the heart of cultural splendor in Dambulla, where ancient history meets modern exploration. Uncover the marvels of the UNESCO-listed Dambulla Cave Temple, meander through vibrant markets, and savor the unique fusion of tradition and innovation in this enchanting Sri Lankan town.
Dambulla Golden Temple
Dambulla cave temple also known as the Golden Temple of Dambulla is a World Heritage Site (1991) in Sri Lanka, situated in the central part of the country. This site is situated 148 kilometres (92 mi) east of Colombo, 72 kilometres (45 mi) north of Kandy and 43 km (27 mi) north of Matale.
Dambulla is the largest and best-preserved cave temple complex in Sri Lanka. The rock towers 160 m over the surrounding plains. There are more than 80 documented caves in the surrounding area. Major attractions are spread over five caves, which contain statues and paintings. These paintings and statues are related to Gautama Buddha and his life. There are a total of 153 Buddha statues, three statues of Sri Lankan kings and four statues of gods and goddesses. The latter include Vishnu and the Ganesha. The murals cover an area of 2,100 square metres (23,000 sq ft). Depictions on the walls of the caves include the temptation by the demon Mara, and Buddha's first sermon.
Prehistoric Sri Lankans would have lived in these cave complexes before the arrival of Buddhism in Sri Lanka as there are burial sites with human skeletons about 2700 years old in this area, at Ibbankatuwa near the Dambulla cave complexes.
This temple complex dates back to the first century BCE. It has five caves under a vast overhanging rock, carved with a drip line to keep the interiors dry. In 1938 the architecture was embellished with arched colonnades and gabled entrances. Inside the caves, the ceilings are painted with intricate patterns of religious images following the contours of the rock. There are images of the Lord Buddha and bodhisattvas, as well as various gods and goddesses.
The Dambulla cave monastery is still functional and remains the best-preserved ancient edifice in Sri Lanka. This complex dates from the third and second centuries BC, when it was already established as one of the largest and most important monasteries. Valagamba of Anuradhapura is traditionally thought to have converted the caves into a temple in the first century BC. Exiled from Anuradhapura, he sought refuge here from South Indian usurpers for 15 years. After reclaiming his capital, the King built a temple in thankful worship. Many other kings added to it later and by the 11th century, the caves had become a major religious centre and still are. Nissanka Malla of Polonnaruwa gilded the caves and added about 70 Buddha statues in 1190. During the 18th century, the caves were restored and painted by the Kingdom of Kandy.
Conservation at the Dambulla Temple Complex has primarily concentrated on the preservation of its mural schemes. Senake Bandaranayake reports that the schemes were cleaned during an initial conservation project during the 1960s which involved the cleaning of the murals and the application of a protective coating.
Subsequent conservation strategies at the Dambulla Temple Complex (mainly since 1982) have focussed on maintaining the integrity of the existing complex which has remained unaltered since the reconstruction of the temple veranda in the 1930s. This strategy was agreed during a collaborative project between UNESCO, The Cultural Triangle Project of Sri Lanka and the Temple Authorities of Dambulla which ran from 1982-1996.
About Matale District
Matale is a town in the hill country of Sri Lanka. The Knuckles Mountain Range is a special landmark of Matale.The Matale administrative district also contains the historic Sigiriya rock castle, Aluvihare Temple and Dambulla Cave Temple . Surrounding the town are the Knuckles foothills called Wiltshire. It is a mainly agricultural area, where tea, rubber, vegetable and spice cultivation dominate.
The Aluvihare Temple, on the North side of the town, is the historic location where the Pali Canon was first written down completely in text on ola (palm) leaves. Situated near Aluvihare are numerous monastery caves, some of which exhibit fine frescoes.
About Central Province
The Central Province of Sri Lanka consists primarily of mountainous terrain. The province has an area of 5,674 km², and a population of 2,421,148. Some major towns include Kandy, Gampola (24,730), Nuwara Eliya and Bandarawela. The population is a mixture of Sinhalese, Tamil and the Moors.
Both the hill capital Kandy and the city of Nuwara Eliya are located within the Central Province as well as Sri Pada. The province produces much of the famous Ceylon tea, planted by the British in the 1860s after a devastating disease killed all the coffee plantations in the province. Central Province attracts many tourists, with hill station towns such as Kandy, Gampola, Hatton and Nuwara Eliya. Temple tooth or Dalada maligawa is the main sacred place in Centrel province.
The climate is cool, and many areas about 1500 meters often have chilly nights. The western slopes are very wet, some places having almost 7000 mm of rain per year. The eastern slopes are parts of the mid-dry zone as it is receiving rain only from North-Eastern monsoon. The Temperatures range from 24°C at Kandy to just 16°C in Nuwara Eliya, which is located 1,889 m above sea level. The highest mountains in Sri Lanka are located in the Central Province. The terrain is mostly mountainous, with deep valleys cutting into it. The two main mountain regions are the central massif and the Knuckles range to the east of Kandy.